Postgres scales
with PgDog
PgDog is the horizontal scaling layer for PostgreSQL.
It can
load balance queries and shard databases,
without application changes.
1docker run ghcr.io/pgdogdev/pgdog:main pgdog \
2 --database-url ${DATABASE_URL}Shard Postgres
without extensions
PgDog operates entirely outside the database and can be deployed
in all environments,
including managed clouds, like AWS RDS and Google Cloud SQL.
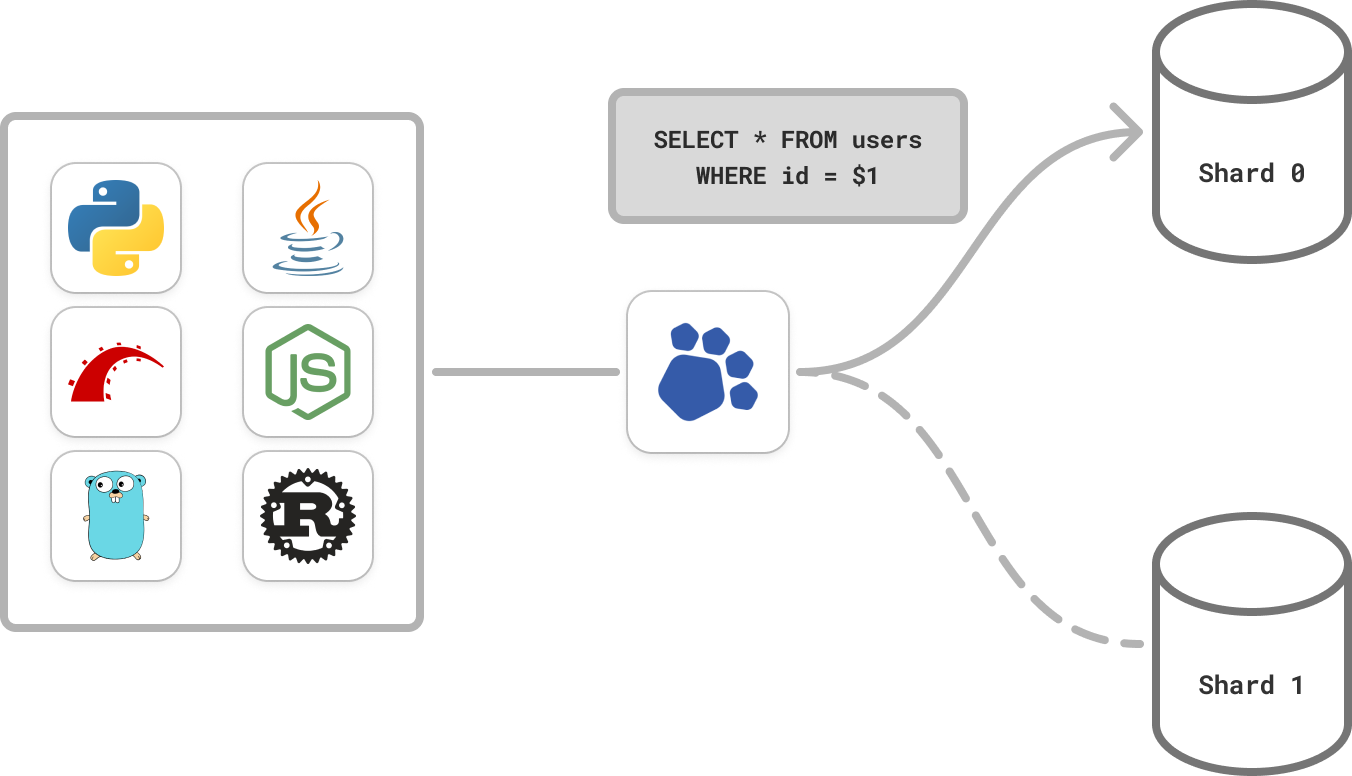
Route queries
PgDog understands SQL and directs queries to the right shards, without having to change your application.
Read more arrow_forward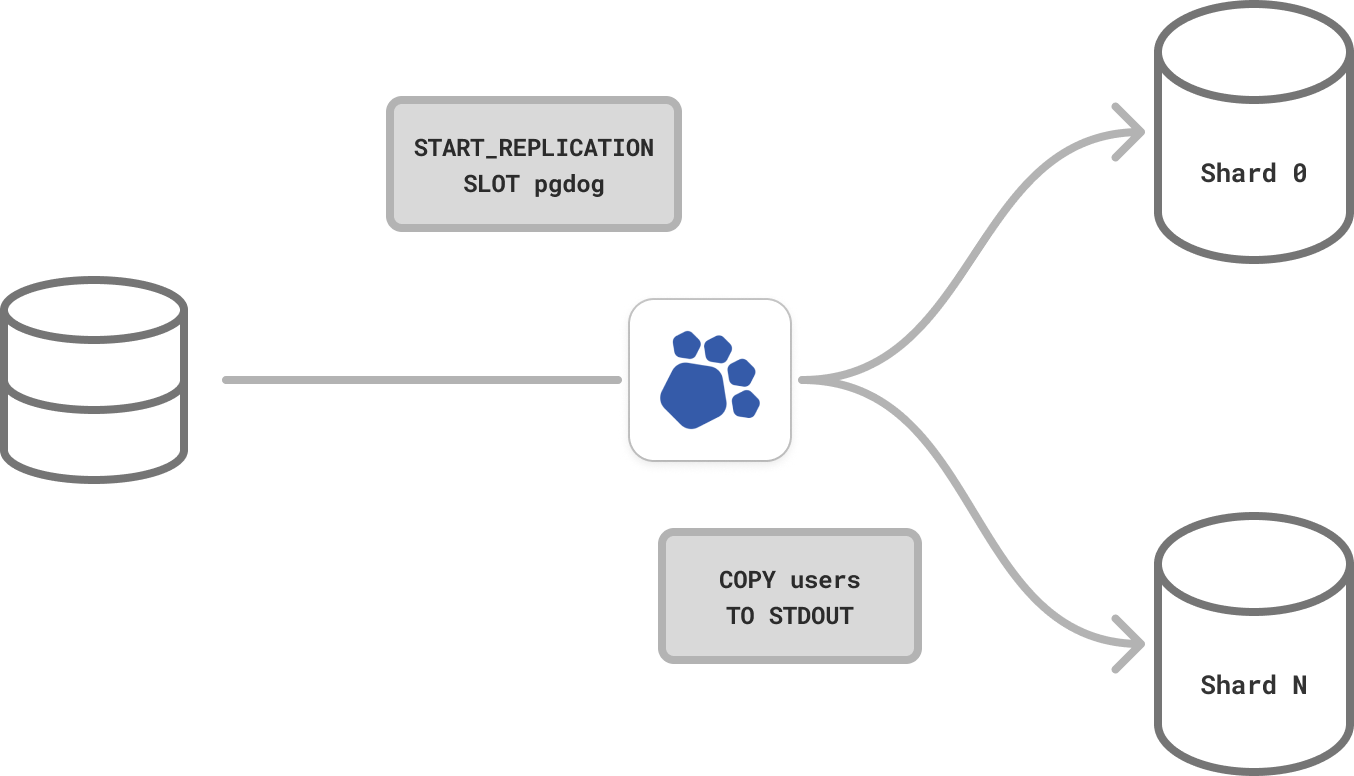
Move data
Using logical replication, PgDog can shard and re-shard tables, in the background and without downtime.
Read more arrow_forwardTrusted by engineers at scale.
Speed of NoSQL
with SQL
Unlock performance previously only available to key/value stores. By adding more data nodes,
Postgres becomes as fast as your hardware.
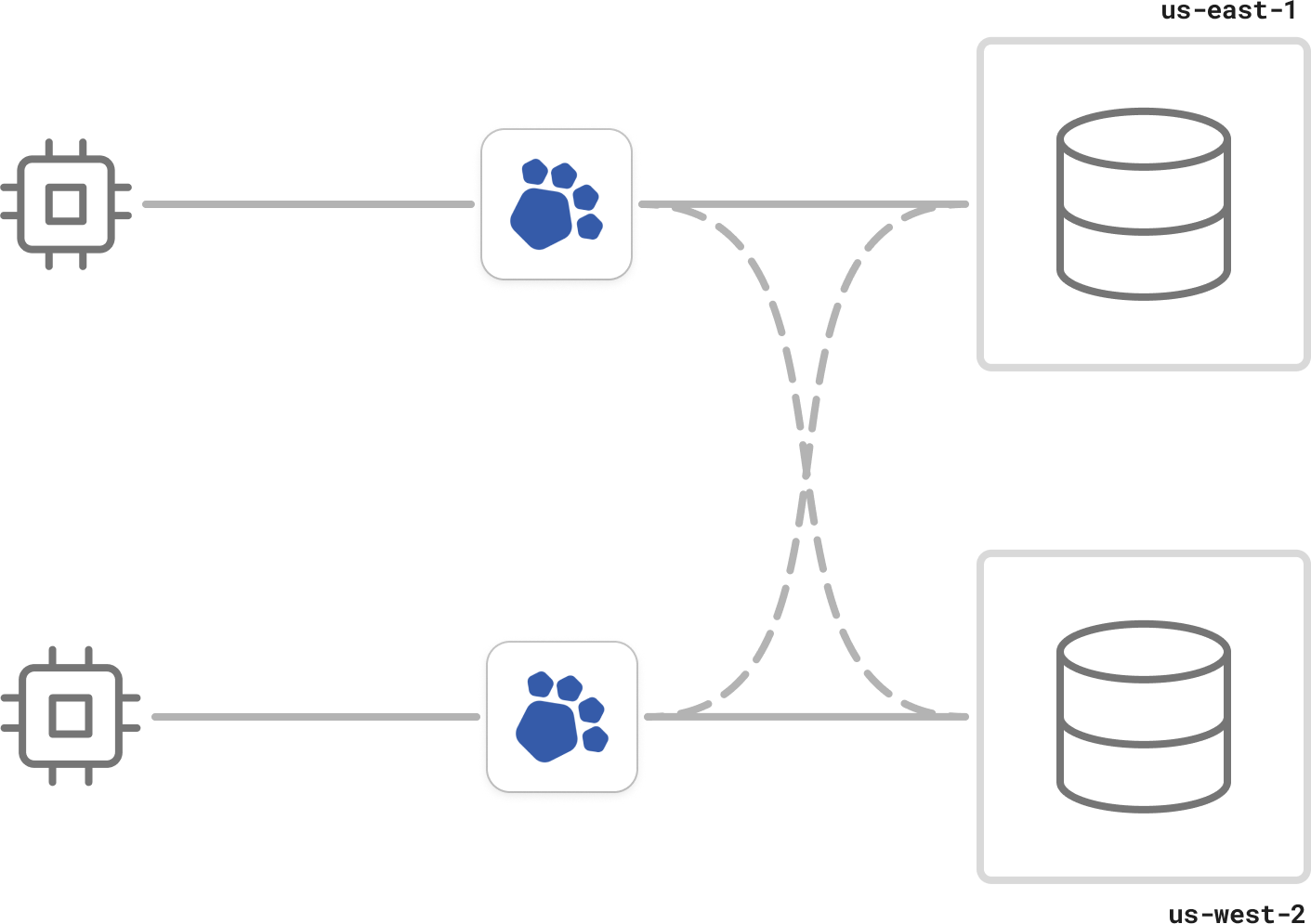
Share-nothing architecture
PgDog nodes are configuration-driven and don't communicate with each other. There are no cross-shard or cross-region dependencies.
Read more arrow_forward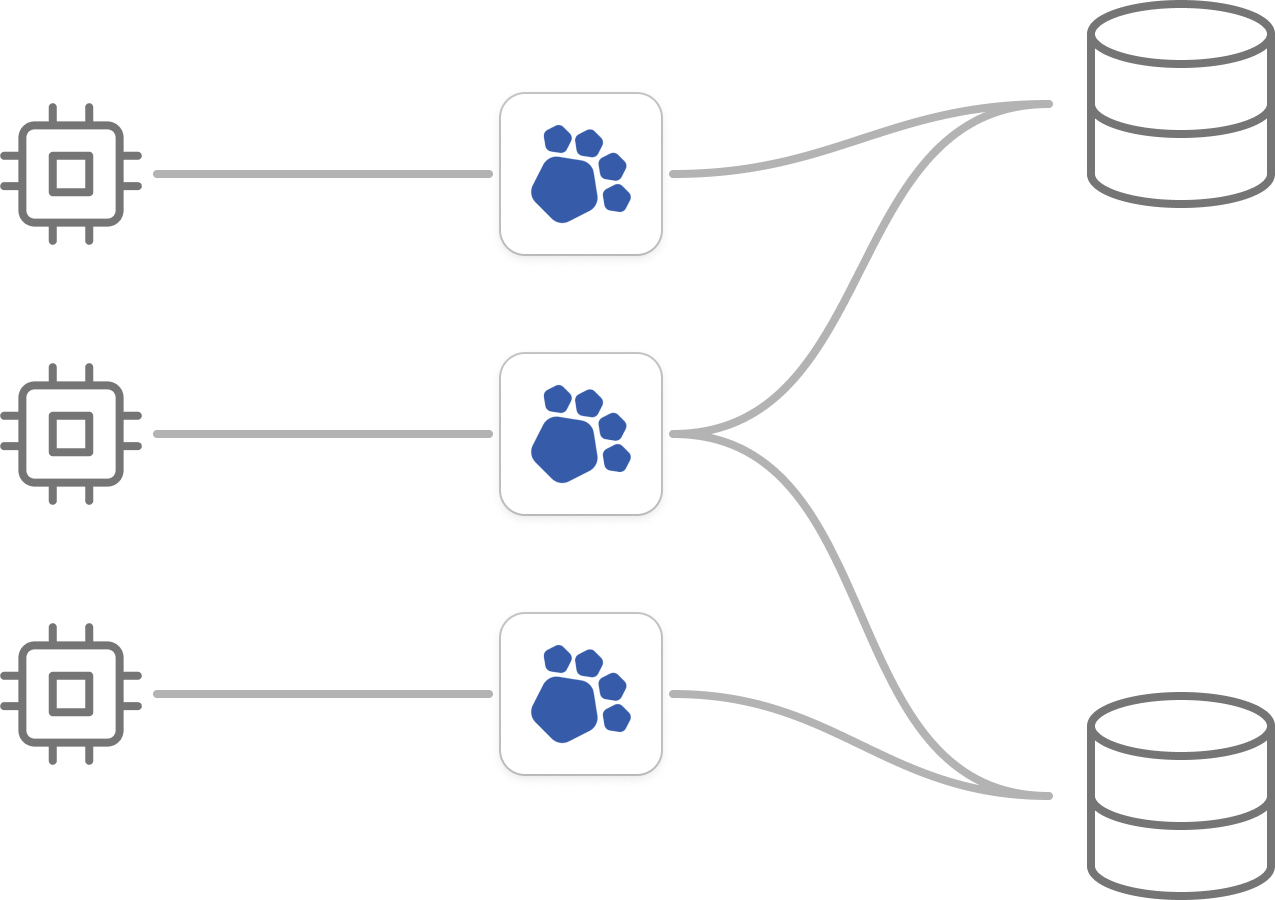
Scalable coordinator
With cross-shard queries supported out of the box, PgDog can be scaled alongside your application.
Read more arrow_forward